Scientific background
Targeted antibody-based therapy for cancer and inflammatory or autoimmune disease
Cantargia develops targeted antibody-based therapy for life-threatening diseases. The type of treatment developed by Cantargia is generally termed immunotherapy and has gained ever-increasing significance over the past decade, particularly in cancer care. Immunotherapy can complement traditional methods of cancer treatment and also has potential for treatment of other diseases, including inflammatory or autoimmune disease.
IL1RAP - An attractive therapeutic target
The molecule IL1RAP (interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein), the target of Cantargia’s most advanced asset nadunolimab (CAN04), is present in most types of cancer, including pancreatic cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer and leukemia. Due to its presence on certain types of immune cells, targeting of IL1RAP is also of interest for treatment of various inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
The advantage of targeted antibody-based immunotherapy is its capability to improve the likelihood of an effective treatment that produces fewer side effects for patients. Cantargia’s goal with CAN04 is clear – to develop a novel drug that, by itself or in combination with other drugs, can form an important part of future cancer treatment. In parallel, Cantargia is developing other IL1RAP-binding antibodies outside the field of cancer, such as the candidate drug CAN10.
For more information on CAN04, see the video below:
Immunotherapy with a unique dual mechanism of action
Cantargia’s technology platform is based on the development of antibodies targeting IL1RAP, which plays a central role in the development of cancer. Cantargia’s principal candidate, CAN04, is unique in the sense that it has a dual mechanism of action: In addition to locating cancer cells and stimulating our natural immune system to destroy such cells, CAN04 also blocks signals which contribute to tumor development and growth.
By binding IL1RAP, CAN04 stimulates the body's killer cells to find and destroy the cancer cells, or metastatic cancer cells. At the same time, CAN04 blocks the signal paths of interleukin-1 (IL-1) on tumor-promoting immune cells exploited by the tumor for growth and for defense from other immune cells. CAN04 blocks the signaling from both forms of IL-1, alpha and beta. This is a key feature of CAN04 as both forms of IL-1 contribute to tumor growth and tumor resistance to chemotherapy.
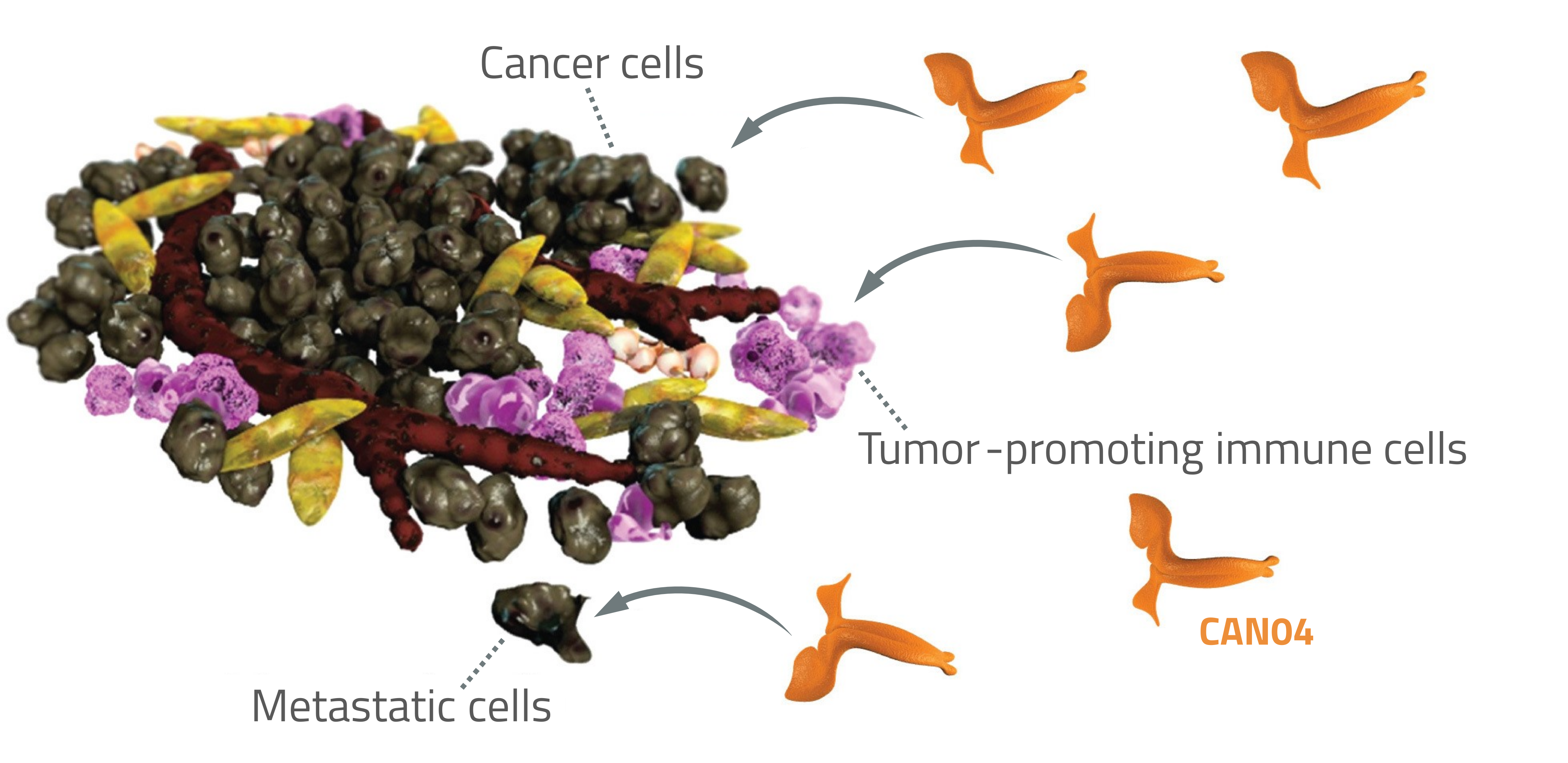
CAN04 has a dual mechanism of action which results in killing of cancer cells, or metastatic cancer cells, and counteracts the function of tumor-promoting immune cells.
Inflammatory/autoimmune diseases the next area for development
Aside from cancer, the IL-1 system plays a central role in the development of a number of severe life-threatening diseases, such as inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. New antibodies with unique properties in terms of blocking signaling paths not only for IL-1, but also IL-33 and IL-36, which also signal with help from IL1RAP, could be used in the treatment of such diseases.
Cantargia recently reached clinical development stage of a second IL1RAP-targeting antibody with the candidate name CAN10. CAN10 is being developed with unique properties that also include a potent blockade of IL-33 and IL-36 signaling, which is beneficial for the treatment of myocarditis and systemic sclerosis. Cantargia’s antibody platform, CANxx, also provides future possibilities to develop unique IL1RAP-targeting antibodies for treatment of other diseases as well.

